Exploring Francophone Countries Of Africa: A Comprehensive Guide
The Francophone countries of Africa represent a vibrant tapestry of cultures, languages, and histories that have been shaped by French colonial influence. With a significant portion of the African continent speaking French, these nations play a crucial role in the global Francophonie. This article delves deep into the characteristics, cultural richness, and socio-economic aspects of Francophone Africa, providing a thorough understanding of these unique regions.
In this exploration, we will cover the geographical distribution of Francophone countries in Africa, their historical context, cultural contributions, and the challenges they face. By the end of this article, readers will gain valuable insights into the significance of these countries in the global landscape.
With over 30 countries in Africa classified as Francophone, understanding this linguistic and cultural phenomenon is essential. Join us as we embark on this enlightening journey through the Francophone countries of Africa.
Table of Contents
- 1. Geographical Distribution of Francophone Countries
- 2. Historical Context of Francophone Africa
- 3. Cultural Richness of Francophone Countries
- 4. Economic Challenges in Francophone Africa
- 5. Education and Language Policies
- 6. Political Landscape in Francophone Countries
- 7. Notable Francophone Countries in Africa
- 8. Future Outlook for Francophone Africa
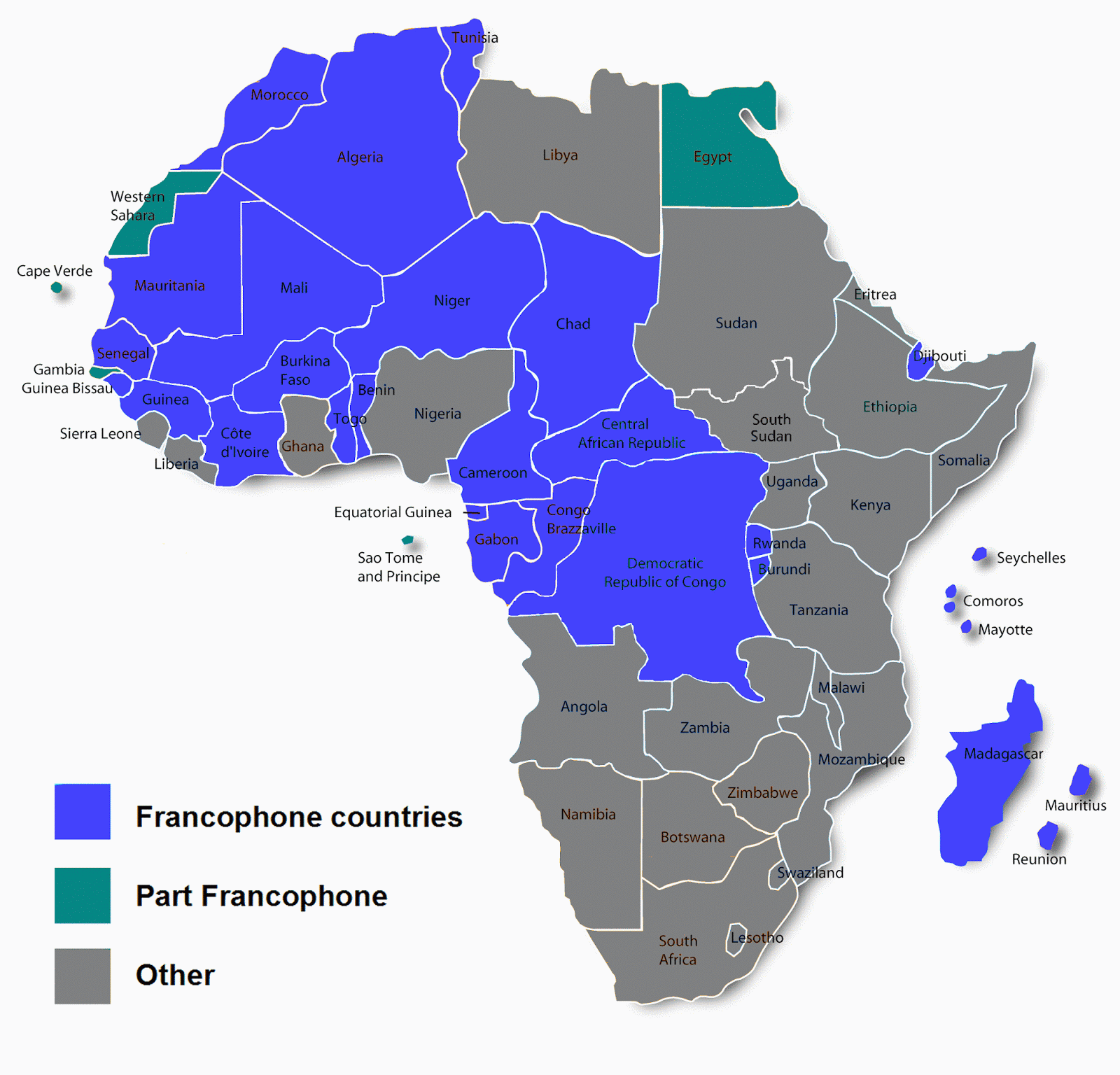
1. Geographical Distribution of Francophone Countries
African Francophone countries are primarily located in West and Central Africa. The term "Francophone" refers to countries where French is a significant language of communication. Below is a list of key Francophone countries in Africa:
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
- Senegal
- Madagascar
- Cameroon
- Burkina Faso
- Niger
- Mali
These countries vary in size, population, and cultural diversity, yet all share the commonality of French linguistic heritage.
2. Historical Context of Francophone Africa
The history of Francophone Africa is largely shaped by colonialism. During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, many African nations were colonized by France. This period left a lasting impact on the political, social, and economic structures of these countries.
Colonial Legacy
French colonial rule introduced the French language and culture, which became dominant in administration, education, and the legal system. Following independence in the mid-20th century, many countries retained French as an official language, a decision that has had both positive and negative implications for national identity and unity.
3. Cultural Richness of Francophone Countries
Francophone Africa is a mosaic of diverse cultures, traditions, and artistic expressions. From literature to music and visual arts, the influence of French culture blends with local customs to create a unique cultural identity.
Literature and Arts
Writers such as Léopold Sédar Senghor and Ahmadou Kourouma have made significant contributions to Francophone literature, addressing themes of identity, colonialism, and post-colonialism. The arts scene is thriving, with music genres such as Afrobeat and Maloya gaining international acclaim.
- Music: Artists like Salif Keita and Youssou N'Dour have popularized African music worldwide.
- Visual Arts: The contemporary art scene is flourishing, with many Francophone African artists gaining recognition on the global stage.
4. Economic Challenges in Francophone Africa
Despite the rich cultural heritage, many Francophone African countries face significant economic challenges. Issues such as poverty, unemployment, and reliance on agriculture are prevalent.
Economic Indicators
According to the World Bank, many of these nations struggle with low GDP per capita and high rates of unemployment. Countries like Niger and Mali have some of the lowest Human Development Index (HDI) scores, highlighting the urgent need for economic development and reform.
5. Education and Language Policies
The role of education in Francophone countries is crucial for development. French is often the medium of instruction, which can pose challenges for students who speak local languages at home.
Language and Education
Many countries are now adopting bilingual education policies to bridge the gap between local languages and French. This approach aims to improve literacy rates and educational outcomes.
6. Political Landscape in Francophone Countries
The political landscape in Francophone Africa is diverse, with countries experiencing varying degrees of stability and democratic governance. Some nations have made significant strides towards democracy, while others remain under authoritarian rule.
Political Challenges
Issues such as corruption, political instability, and human rights violations are ongoing challenges in many countries. However, there is a growing movement towards democratic reforms and civil society engagement.
7. Notable Francophone Countries in Africa
While many countries contribute to the Francophone community, a few stand out due to their historical significance, cultural impact, and economic potential.
- Democratic Republic of the Congo: The largest Francophone country in Africa, known for its rich natural resources.
- Côte d'Ivoire: An economic powerhouse in West Africa, famous for its cocoa production.
- Senegal: A cultural hub, renowned for its music, arts, and vibrant democracy.
8. Future Outlook for Francophone Africa
The future of Francophone Africa is filled with potential. As globalization continues to influence the continent, there is an opportunity for economic growth, cultural exchange, and strengthened international ties.
Opportunities for Growth
With a young and growing population, Francophone Africa has the potential to become a significant player in the global economy. Investments in education, technology, and infrastructure can pave the way for sustainable development.
Conclusion
In summary, the Francophone countries of Africa offer a rich and diverse landscape characterized by cultural heritage, historical significance, and economic challenges. Understanding these nations' complexities is essential for recognizing their role in the global community.
We encourage you to share your thoughts in the comments below, explore more articles on this topic, and engage with the vibrant culture of Francophone Africa.
Final Thoughts
We hope this comprehensive guide has provided valuable insights into the Francophone countries of Africa. We invite you to return for more informative articles that explore the rich tapestry of cultures around the world.
Article Recommendations
- Lookmovie
- Dafne Keen Nudes
- Hdhub4u
- Samantha Hegseth
- Aliyah Marie Nude
- Aishah Hasnie No Makeup
- Did Will Smith Die
- Jameliz Nudes
- Dan Bongino Wife Accident
- Nate Silver Net Worth